
Study of mesenchymal stromal cells from human placenta for applications in regenerative medicine and possible hepatic therapies
Brief description
Patients with liver cirrhosis have an increased risk of developing multiple organ failure due to infections caused by bacterial translocation caused by the passage of bacteria and their products, such as endotoxins, from the lumen to the intestinal wall and from the mesenteric lymph nodes to the bloodstream.
Bacteria and their products are able to activate the immune system with increased release of mediators capable of inducing the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) whose progression culminates in multiple organ failure (MOF).
The functional alterations of the bacterial defenses of nonspecific and cell-mediated humoral immunity facilitate the engraftment of infections in the various sites, including ascitic fluid with the risk of developing PBS (Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis).
Impact:
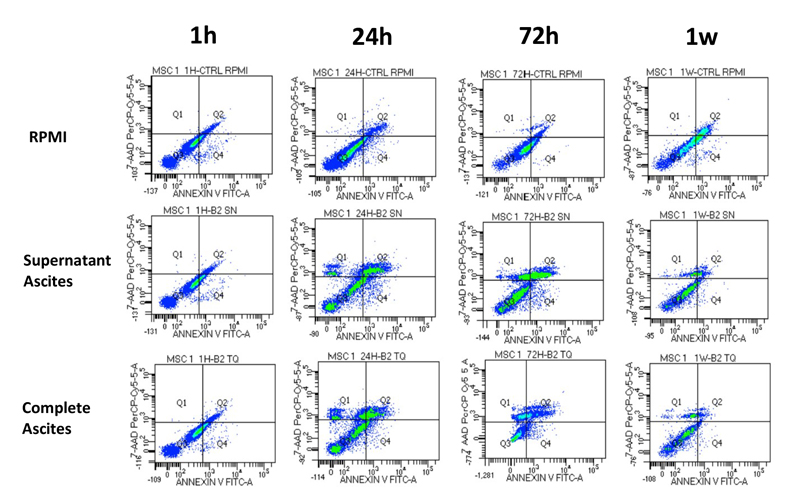
In patients with advanced cirrhosis, DNA-bacterial translocation induces the activation of the complement system in both plasma and ascitic fluid and activates the cell-mediated immune response and the overproduction of nitric oxide by peritoneal macrophages with a higher production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α). Macrophages, innate immunity cells, represent the first line of defense against microbes and could be used as targets for the treatment of ascites in basal conditions or in the presence of over infection.
The obtained results could be the basis to further investigate the therapeutic role of hA-MSCs in bacterial clearance and macrophage phagocytosis as well as their cross talk with immune cells in SBP.
Pipeline
-
CLINICAL
NEED -
DISEASES
ANALYSIS - DISCOVERY
-
PRECLINICAL
VALIDATION -
PRECLINICAL
DEVELOPMENT -
CLINICAL
STUDIES
Principal Investigator
Contact
Therapeutic area:
Products:
ATMP (Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products)
Collaborations:
- Istituto Mediterraneo per i Trapianti e Terapie ad Alta Specializzazione (IRCCS ISMETT), Palermo, Italia
Scarica il pdf del progetto
